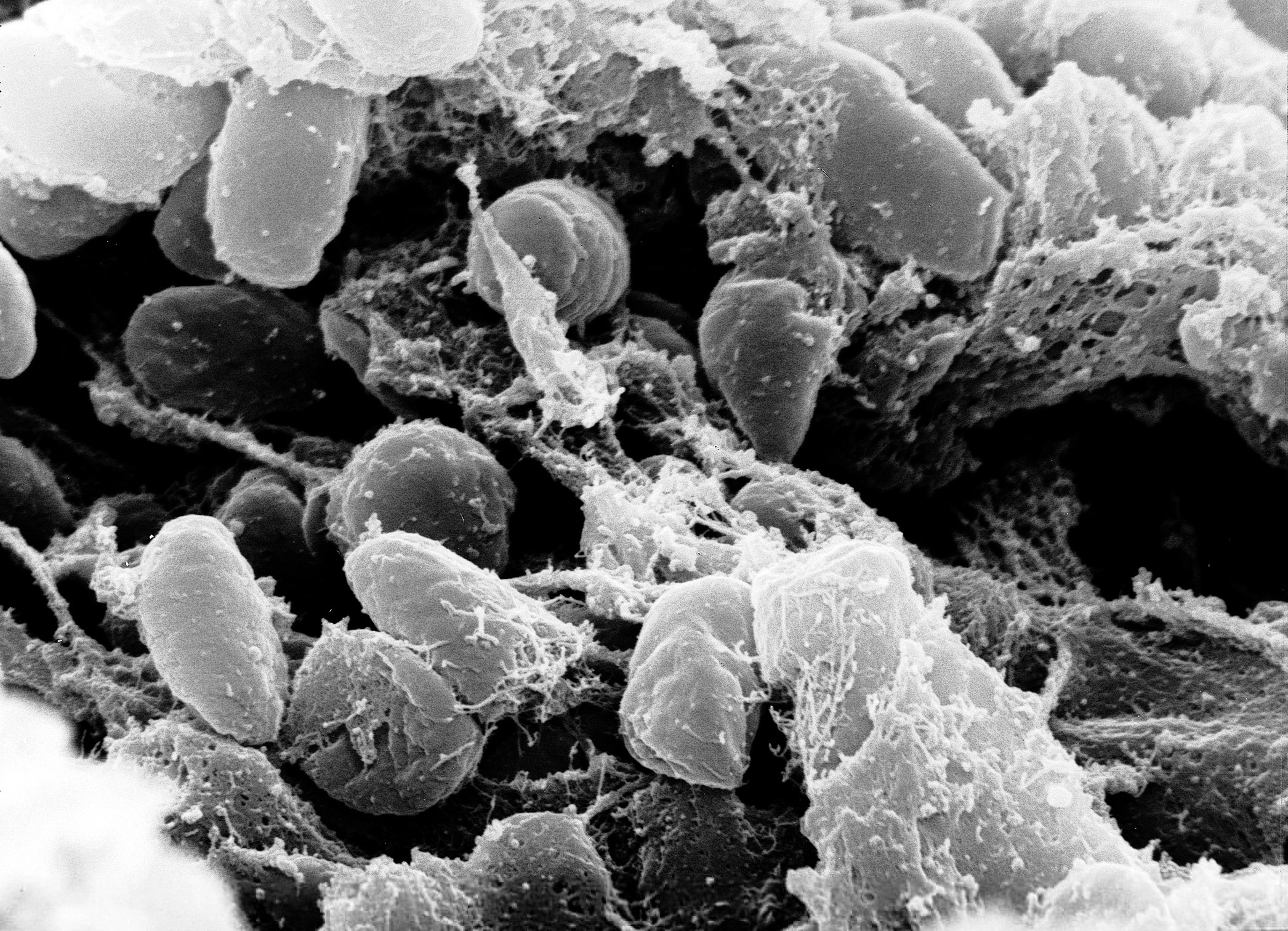
 Last year, I reviewed a PLoS Pathogens paper that found European Black Plague victims from the mid 14th century were infected with more than one clone of Yersinia pestis. While the Y. pestis-specific sequences amplified from several skeletal samples from various countries were evidence of the bacterium as the etiological agent, questions still remained about the virulence of the outbreak. What allowed that ancient strain of Y. pestis to cause such widespread death? Another group of researchers decided to further analyze the causative agent of the Black Plague by enriching for and sequencing one of the extrachromasomal plasmids present in the bacterial genome: the 9.6kb virulence-associated pPCP1 plasmid. Continue reading “Dance Macabre: Will 14th Century Remains Reveal the Pandemic Secrets of the Black Death?”
Last year, I reviewed a PLoS Pathogens paper that found European Black Plague victims from the mid 14th century were infected with more than one clone of Yersinia pestis. While the Y. pestis-specific sequences amplified from several skeletal samples from various countries were evidence of the bacterium as the etiological agent, questions still remained about the virulence of the outbreak. What allowed that ancient strain of Y. pestis to cause such widespread death? Another group of researchers decided to further analyze the causative agent of the Black Plague by enriching for and sequencing one of the extrachromasomal plasmids present in the bacterial genome: the 9.6kb virulence-associated pPCP1 plasmid. Continue reading “Dance Macabre: Will 14th Century Remains Reveal the Pandemic Secrets of the Black Death?”
XWe use cookies and similar technologies to make our website work, run analytics, improve our website, and show you personalized content and advertising. Some of these cookies are essential for our website to work. For others, we won’t set them unless you accept them. To learn more about our approach to Privacy we invite you to Read More
By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However you may visit Cookie Settings to provide a controlled consent.
RejectCookie settingsACCEPT ALL
By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However you may visit Cookie Settings to provide a controlled consent.
RejectCookie settingsACCEPT ALL
Manage consent
Privacy Overview
We use cookies and similar technologies to make our website work, run analytics, improve our website, and show you personalized content and advertising. Some of these cookies are essential for our website to work. For others, we won’t set them unless you accept them. To find out more about cookies and how to manage cookies, read our Cookie Policy.
If you are located in the EEA, the United Kingdom, or Switzerland, you can change your settings at any time by clicking Manage Cookie Consent in the footer of our website.
If you are located in the EEA, the United Kingdom, or Switzerland, you can change your settings at any time by clicking Manage Cookie Consent in the footer of our website.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Advertisement". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| gdpr_status | 6 months 2 days | This cookie is set by the provider Media.net. This cookie is used to check the status whether the user has accepted the cookie consent box. It also helps in not showing the cookie consent box upon re-entry to the website. |
| lang | This cookie is used to store the language preferences of a user to serve up content in that stored language the next time user visit the website. | |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SC_ANALYTICS_GLOBAL_COOKIE | 10 years | This cookie is associated with Sitecore content and personalization. This cookie is used to identify the repeat visit from a single user. Sitecore will send a persistent session cookie to the web client. |
| vuid | 2 years | This domain of this cookie is owned by Vimeo. This cookie is used by vimeo to collect tracking information. It sets a unique ID to embed videos to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 24 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
| _ga | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. The cookie is used to calculate visitor, session, campaign data and keep track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookies store information anonymously and assign a randomly generated number to identify unique visitors. |
| _gid | 1 day | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. The cookie is used to store information of how visitors use a website and helps in creating an analytics report of how the website is doing. The data collected including the number visitors, the source where they have come from, and the pages visted in an anonymous form. |
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IDE | 1 year 24 days | Used by Google DoubleClick and stores information about how the user uses the website and any other advertisement before visiting the website. This is used to present users with ads that are relevant to them according to the user profile. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | This cookie is set by doubleclick.net. The purpose of the cookie is to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | This cookie is set by Youtube. Used to track the information of the embedded YouTube videos on a website. |
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww.promega.com_sitecore | No description | |
| CanCheckOut | No description | |
| CommerceCustomerId | No description | |
| CONSENT | 16 years 7 months 15 days 6 hours 22 minutes | No description |
| cookies.js | session | No description |
| Country | 3 months | No description |
| CountrySelected | 3 months | No description |
| CustomerId | No description | |
| PreferredLanguage | 3 months | No description |
| PromegaCompno | 3 months | No description |
| PromegaCountry | 3 months | No description |
| RememberMe | 6 months | No description |
| SameSite | No description | |
| sc_ext_contact | 2 years | No description |
| sc_ext_session | session | No description |
| TS01ae363a | No description | |
| UID | 2 years | No description |
| website#lang | This cookie is used for storing the visitor language preferences. It heps in delivering localised language version. | |
| wp_api | past | No description |
| wp_api_sec | past | No description |
| _ga_WHZLGVEZ9X | 2 years | No description |
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| YSC | session | This cookies is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos. |
| _gat_UA-62336821-1 | 1 minute | This is a pattern type cookie set by Google Analytics, where the pattern element on the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. It appears to be a variation of the _gat cookie which is used to limit the amount of data recorded by Google on high traffic volume websites. |
