A protein first purified and sold by Promega almost four decades ago has emerged as a crucial tool in many COVID-19 testing workflows. RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor was first released in 1982, only four years after the company was started. At that time, the entire Promega catalog fit on a single sheet of 8.5 × 11” paper, and RNasin was one of the first products to draw widespread attention to Promega. Today, the demand for this foundational product has skyrocketed as it supports labs responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor?
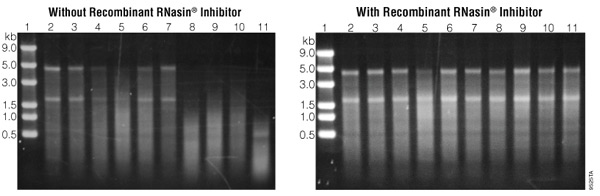
RNA is notoriously vulnerable to contamination by RNases. These enzymes degrade RNA by breaking the phosphodiester bonds forming the backbone of the molecule. To say that RNases are everywhere is barely an exaggeration – almost every known organism produces some form of RNase, and they’re commonly found in all kinds of biological samples. They’re easily introduced into experimental systems, since even human skin secretes a form of RNase. Once they’re present, it’s very hard to get rid of them. Even an autoclave can’t inactivate RNases; the enzymes will refold and retain much of their original activity.
RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor is a protein that has been shown to inhibit many common contaminating RNases, but without disrupting the activity of enzymes like reverse transcriptase that may be essential to an experiment. It works by binding to the RNase enzyme, prevent it from acting on RNA molecules. This is important for ensuring that RNA samples are intact before performing a complex assay.
Continue reading “38 Years After First Release, RNasin Protects COVID-19 Tests”