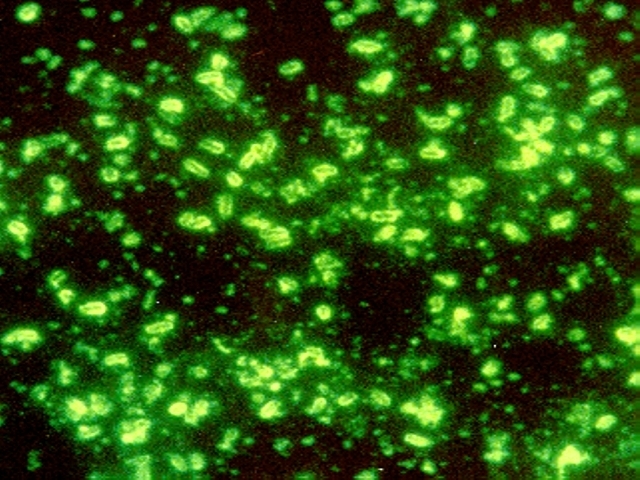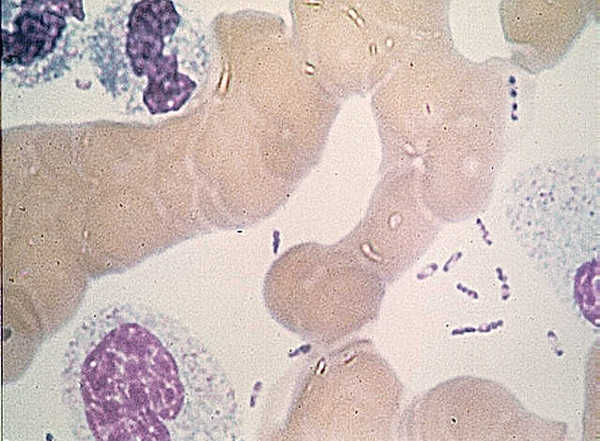
Teeth have been the choice for identifying the infectious agent behind the Plague of Justinian in the sixth century and the Black Plague in the 14th century. In fact, Yersinia pestis, the bacterium responsible for these plagues, has infected humans as far back as the Neolithic. But what can we learn about the pandemic strain or strains of Y. pestis described in historical records? A team of researchers from Europe and the US, many of whom have been delving into the history of Y. pestis for the last decade, wanted to further investigate the Plague of Justinian. They studied bacterial DNA extracted from human remains found in Western European communal graves that were dated to around 541–750, the period of the historically documented Plague of Justinian. Their investigation examined the bacteria’s diversity and how far it spread during this “First Pandemic” of plague. Continue reading “Delving into the Diversity of The Plague of Justinian”