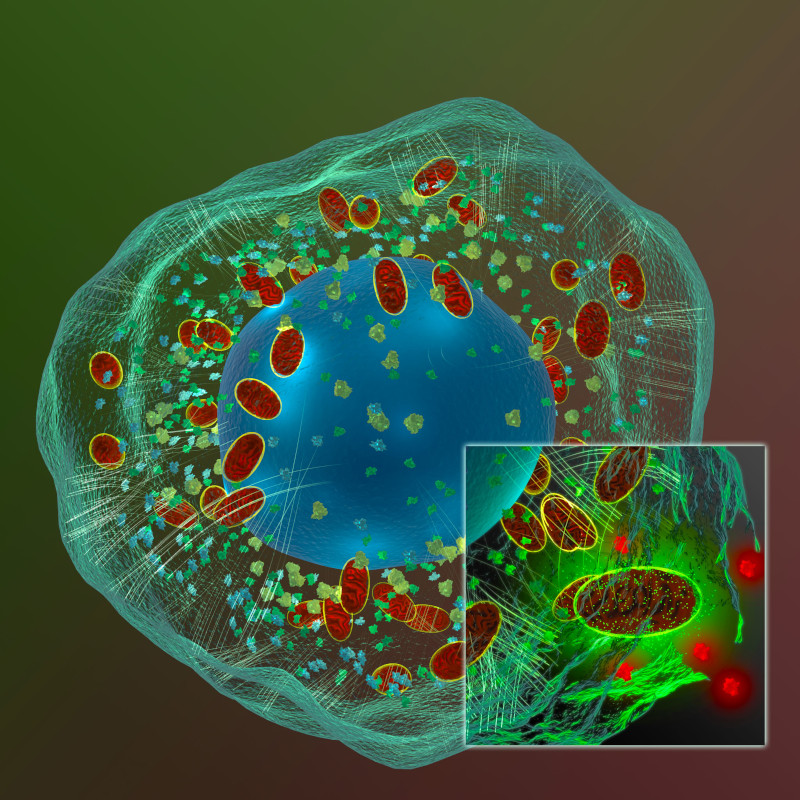
Cancer has been studied for decades by scientists trying to find a vulnerability to exploit and testing compounds to develop as potential drugs. As the “Emperor of All Maladies”, cancer has proven itself to be a wily beast with many varieties of genetic mutations for eluding cellular control, tireless in its ability to divide and spread. In the end, a cancer cell is still a cell and subject to its environment even though cancer does not play by the same rules as the normal cells that exist around it. To be able to grow, a cell needs access to metabolites, molecules needed for building the materials and machinery needed by the cell to function and divide. These requirements also offer potential pathways to target for halting cancer growth and spread.
All cells use glucose to generate ATP, but normal and cancer cells differ in how glucose is converted to ATP. Most cells use glucose in oxidative phosphorylation, but cancer cells use aerobic glycolysis, converting glucose to lactate without oxygen. This Warburg effect (glucose converted to lactate) is a hallmark of cancer cells as they take up glucose at a much higher rate than normal cells. Blocking glucose uptake is one way to target cancer cells. While 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) has been shown to slow glucose uptake in vitro, the compound proved toxic in clinical trials and lower dosages do not seem to be an effective treatment against cancer. While not an ideal drug target, glucose uptake has been helpful in monitoring cancer response to therapies via fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET).
Continue reading “Finding Chinks in the Armor: Cancer’s Need for Metabolites” Like this:
Like Loading...