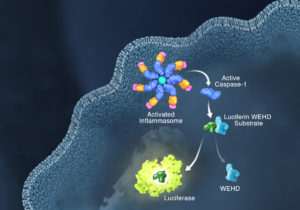
Innate immunity, the first line of immune defense, uses a system of host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to recognize signals of “danger” including invariant pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). These signals in turn recruit and assemble protein complexes called inflammasomes, resulting in the activation of caspase-1, the processing and release of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1ß and IL-18, and the induction of programmed, lytic cell death known as pyroptosis.
Innate immunity and the activity of the inflammasome are critical for successful immunity against a myriad of environmental pathogens. However dysregulation of inflammasome activity is associated with many inflammatory diseases including type 2 diabetes, obesity-induced asthma, and insulin resistance. Recently, aberrant NLRP3 inflammasome activity also has been associated with age-related macular degeneration and Alzheimer disease. Understanding the players and regulators involved in inflammasome activity and regulation may provide additional therapeutic targets for these diseases.
Currently inflammasome activation is monitored using antibody-based techniques such as Western blotting or ELISA’s to detect processed caspase-1 or processed IL-1ß. These techniques are tedious and are only indirect measures of caspase activity. Further, gaining information about kinetics—relating inflammasome assembly, caspase-1 activation and pyroptosis in time—is very difficult using these methods. O’Brien et al. describe a one-step, high-throughput method that enables the direct measurement of caspase-1 activity. The assay can be multiplexed with a fluorescent viability assay, providing information about the timing of cell death and caspase-1 activity from the same sample. Continue reading “Activating the Inflammasome: A New Tool Brings New Understanding”