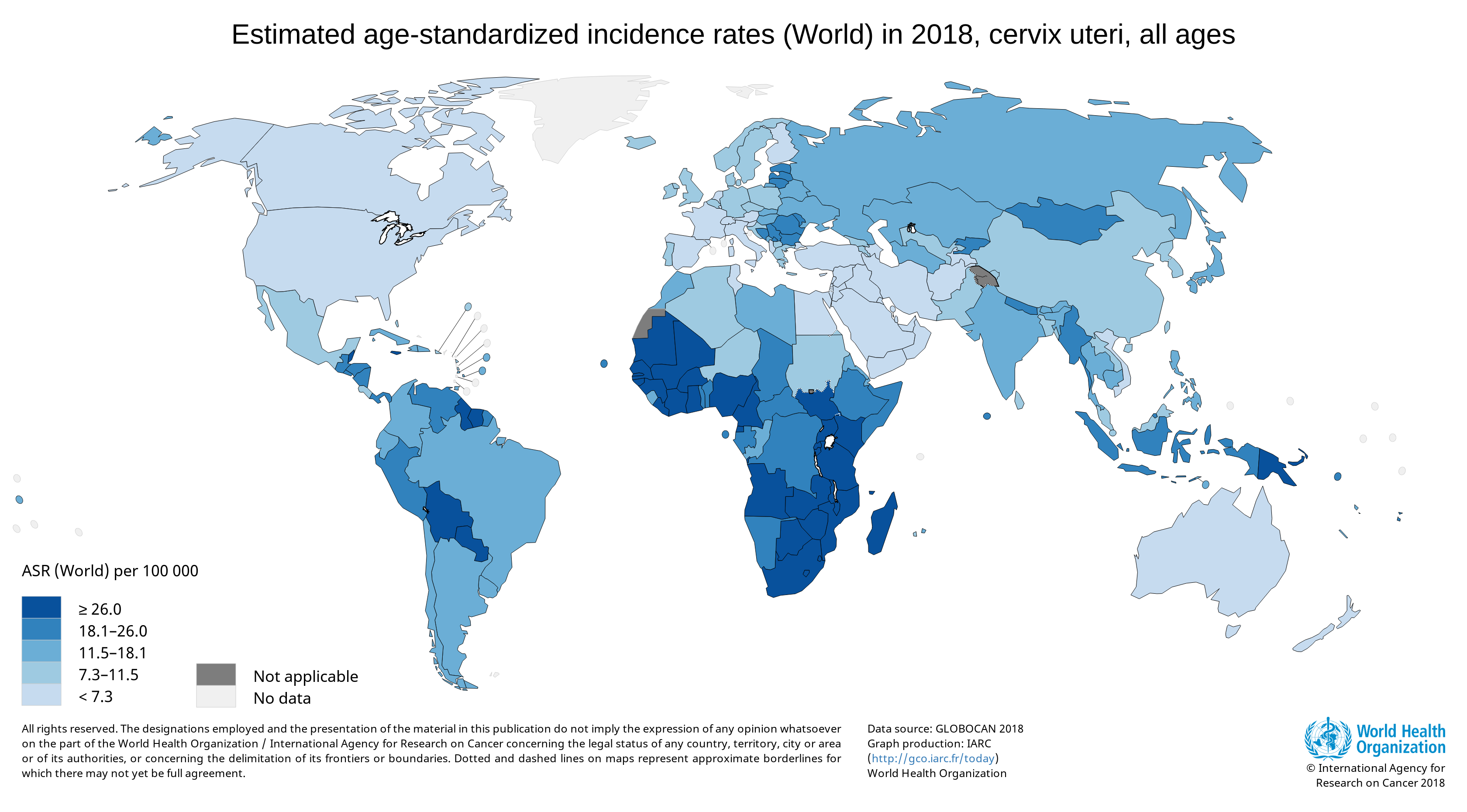
Cervical cancer is a major health problem for women, and it is currently the fourth most common cancer in women globally (1). A worldwide analysis of cancer estimates from the Global Cancer Observatory 2018 database showed that cervical cancer disproportionally affects lower-resource countries, on the basis of their Human Development Index; it was the leading cause of cancer-related death in women in many African countries (1).
Infection by human papillomavirus (HPV), a double-stranded DNA virus, is the leading cause of cervical cancer. Many types of HPV have been identified, and at least 14 high-risk HPV types are cancer-causing, according to a World Health Organization (WHO) fact sheet. Of these types, HPV-16 and HPV-18 are responsible for 70% of cervical cancers and pre-cancerous cervical lesions. HPV infection is sexually transmitted, most commonly by skin-to-skin genital contact. Although the majority of HPV infections are benign and resolve within a year or two, persistent infection in women, together with other risk factors, can lead to the development of cervical cancer [reviewed in (2)].
Continue reading “How Does Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Drive the Progression of Cervical Cancer?”
