Luminescent live-cell assays are powerful tools for cellular biology research. They offer both qualitative and quantitative insights into processes such as gene expression, cell viability, metabolic activity, protein and small molecule interactions, and targeted protein degradation. But what if you could go beyond the numbers and actually see what is happening in your cells? With luminescent imaging, you have the opportunity to uncover more dynamic data by visualizing what happens with your cells in real time.
Why Luminescent Imaging?
Bioluminescent reporters such as NanoLuc® Luciferase reporters are well-suited for use in bioluminescent imaging studies. The extreme brightness means that exposure times can be reduced, compared to the time required for other luminescent reporter proteins. Its small size also makes it less likely to perturb the normal biology or functionality.
Another benefit of bioluminescence for imaging is the inherent stability and sustainability of the bioluminescent signal, which does not require external excitation like fluorescent tags. This allows direct visualization of protein dynamics in living cells without the need for repeated sample excitation. The lack of external excitation also reduces the risk of phototoxicity and photobleaching, common issues that can adversely affect cell viability and signal integrity over time.
Applications Across Cellular Research
Luminescent imaging complements traditional luminescence assays by adding spatial and temporal dimensions. With luminescent live-cell imaging, researchers can visualize NanoLuc® Luciferase assays to gain a deeper understanding of the real-time cellular processes occurring in each experiment. Applications include:
- Determining which cells provide signal
- Analyzing mixed cell populations
- Identifying rare events
- Monitoring protein:protein interactions
- Identifying protein localization and translocation
- Tracking protein degradation and stability over time
- Visualizing ligand:protein interactions (target engagement)
Luminescent Imaging in Action
Targeted Protein Degradation
Selectively targeting proteins for removal from the cell—instead of inhibiting protein activity—is a newer approach with therapeutic potential. In this method, the protein is targeted for degradation using the cell’s natural ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS). The degradation process is initiated by compounds such as molecular glues and proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) linking the target protein to an E3 ligase. Once this linkage occurs, the cell’s UPS does the rest.
Luminescent substrates with increased signal stability, such as the Nano-Glo® Extended Live Cell Substrate, enables researchers to image targeted protein degradation in their cells in real time. In the example shown below, Nano-Glo® Vivazine™ Live Cell Substrate was used to image degradation of the GSPT1 protein by the CC-885 degrader over 5 hours.
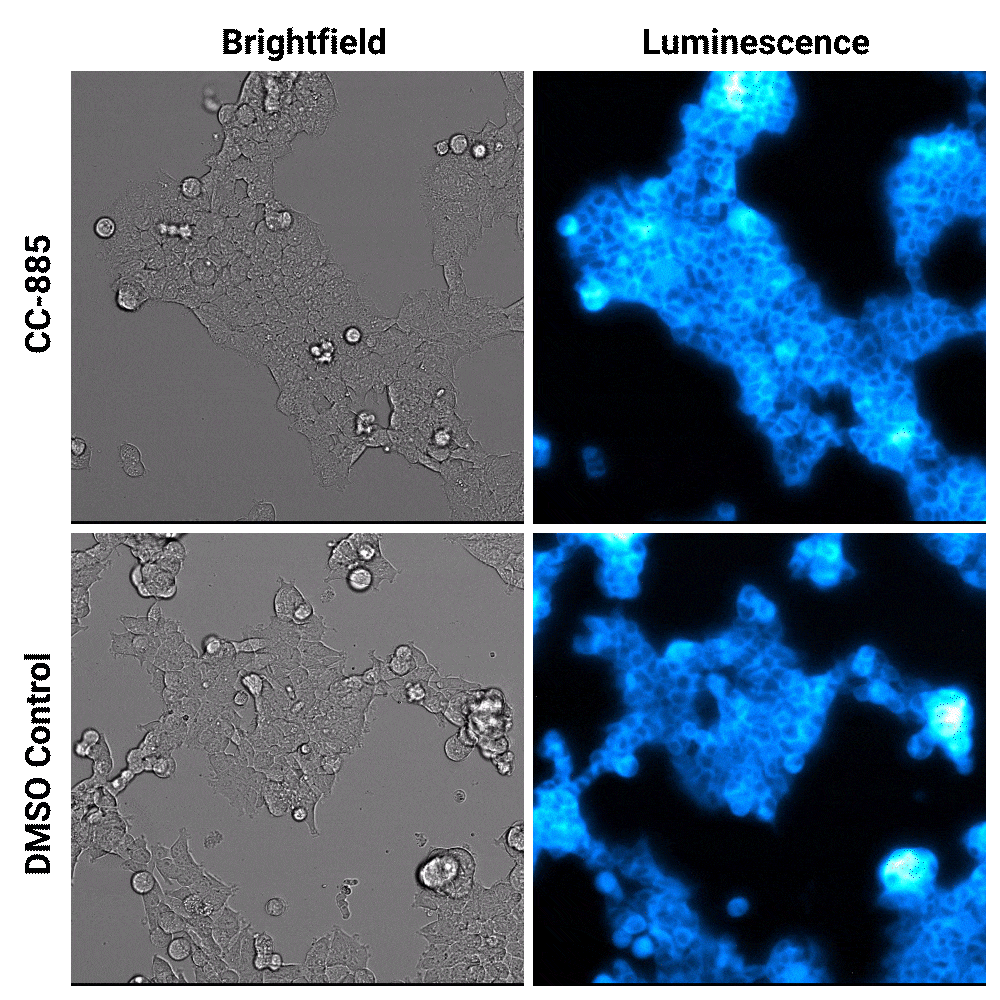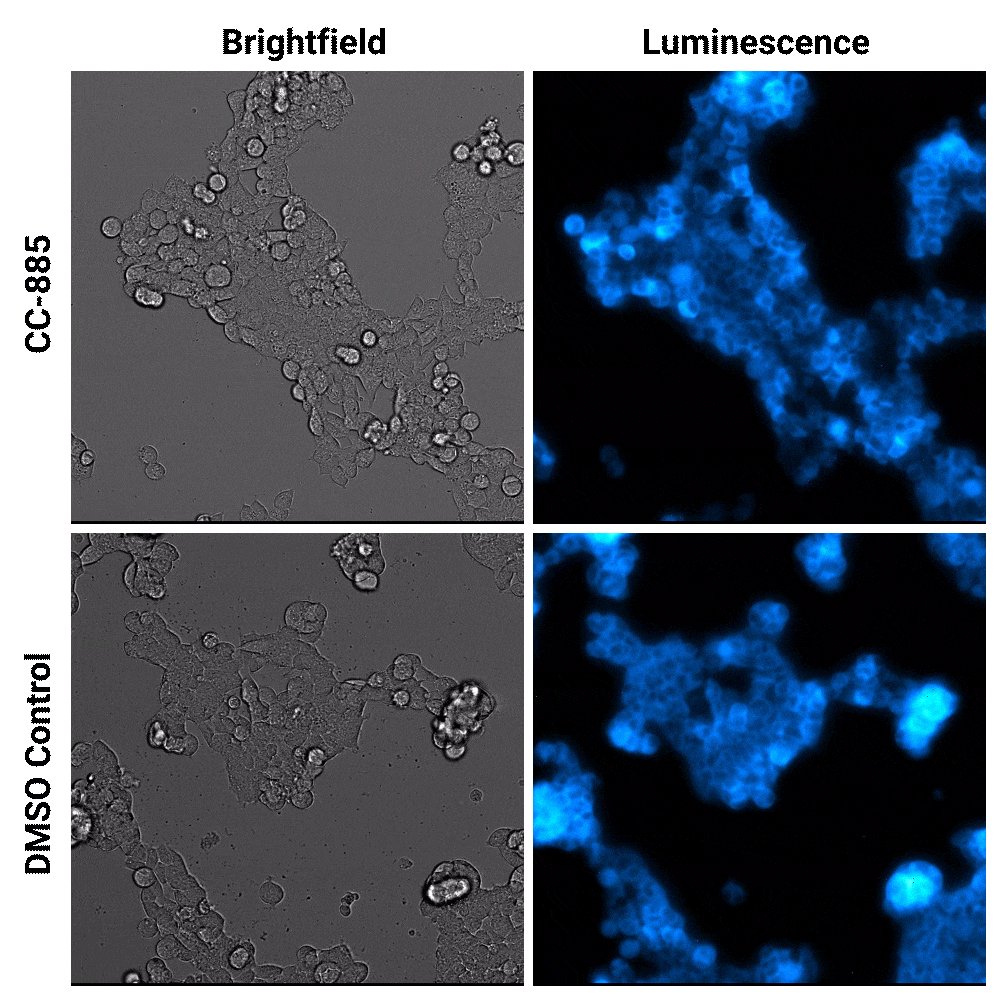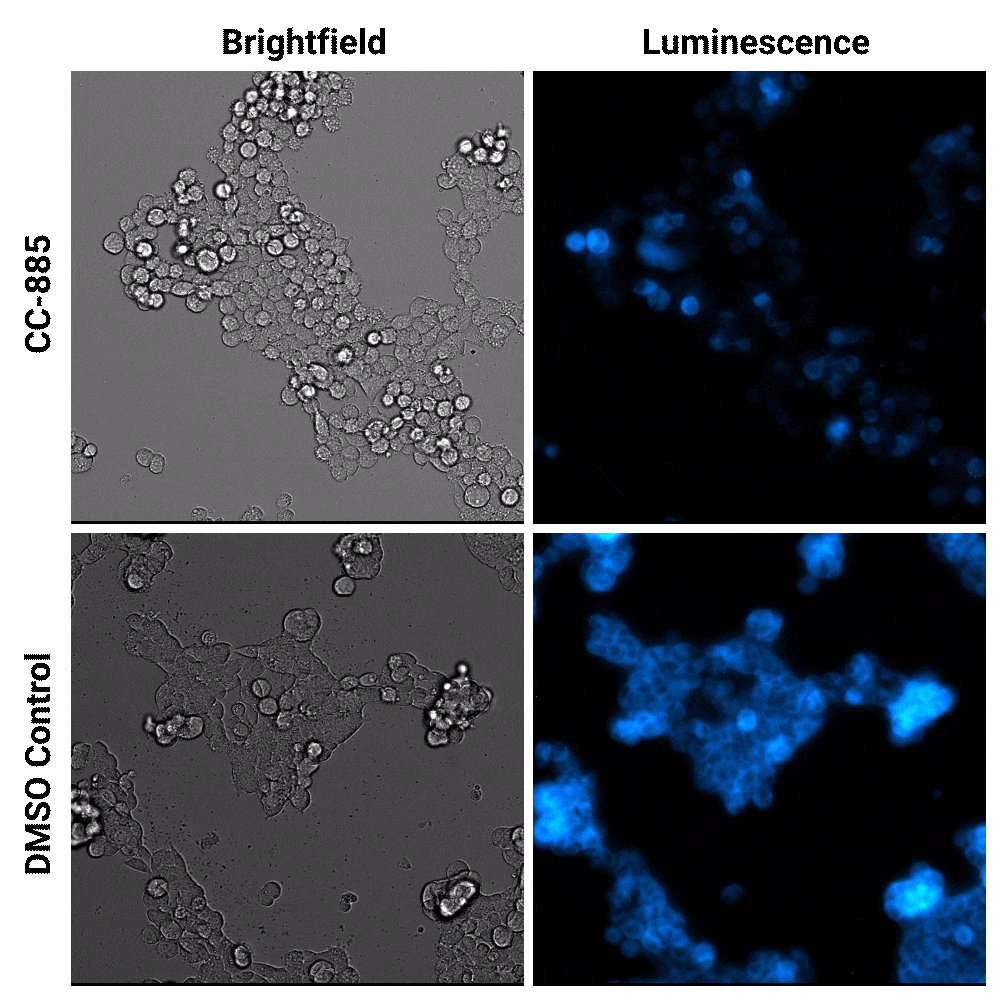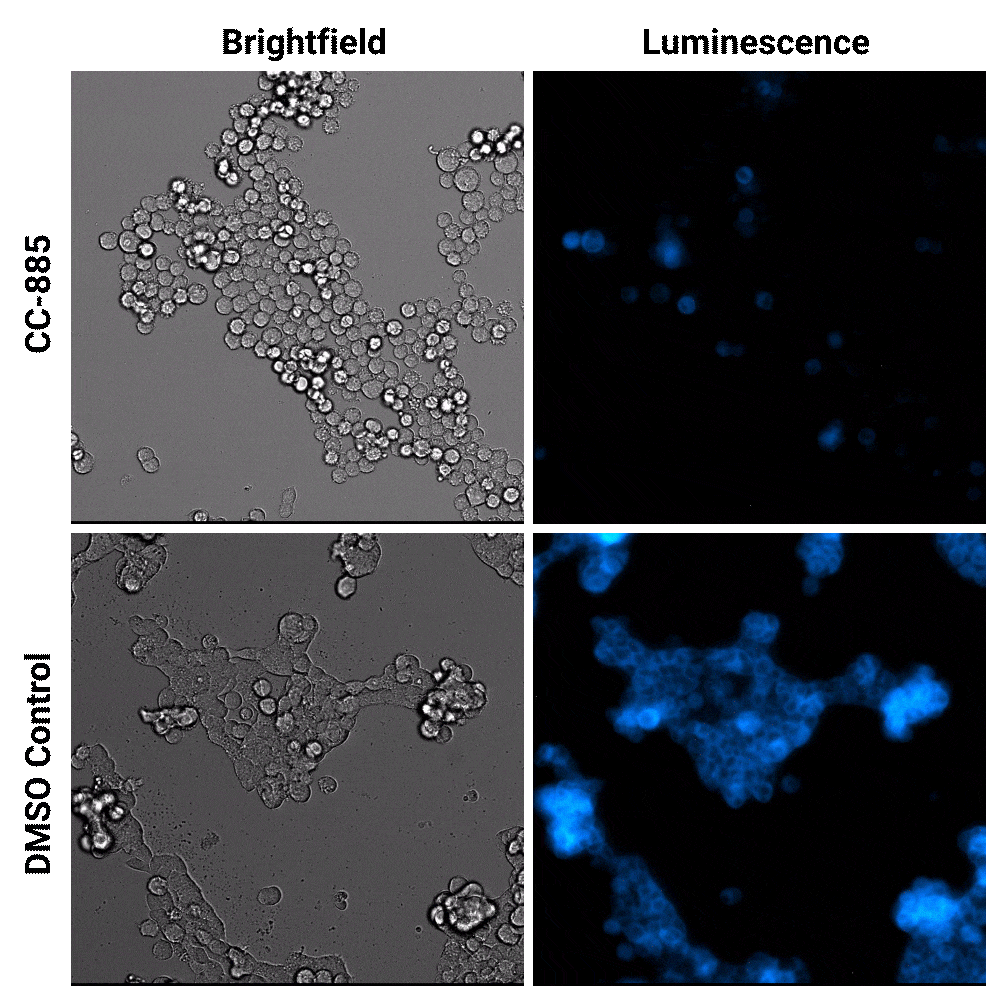
Targeted protein degradation over time. HEK293 cells expressing endogenous HiBiT-tagged GSPT1 and stably expressing LgBiT were treated with CC-885 degrader or DMSO control treatment. Assayed with Nano-Glo® Vivazine™ Live Cell Substrate and imaged over 5 hours using GloMax® Galaxy Bioluminescence Imager.
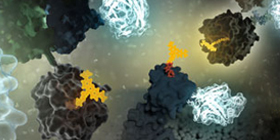
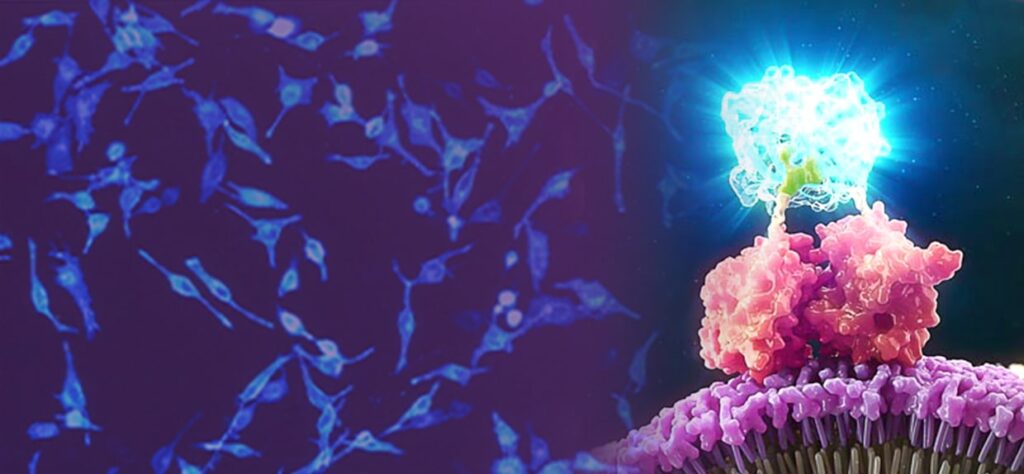
Combining Luminescent and Fluorescent Imaging to Detect Protein:Small Molecule Interactions
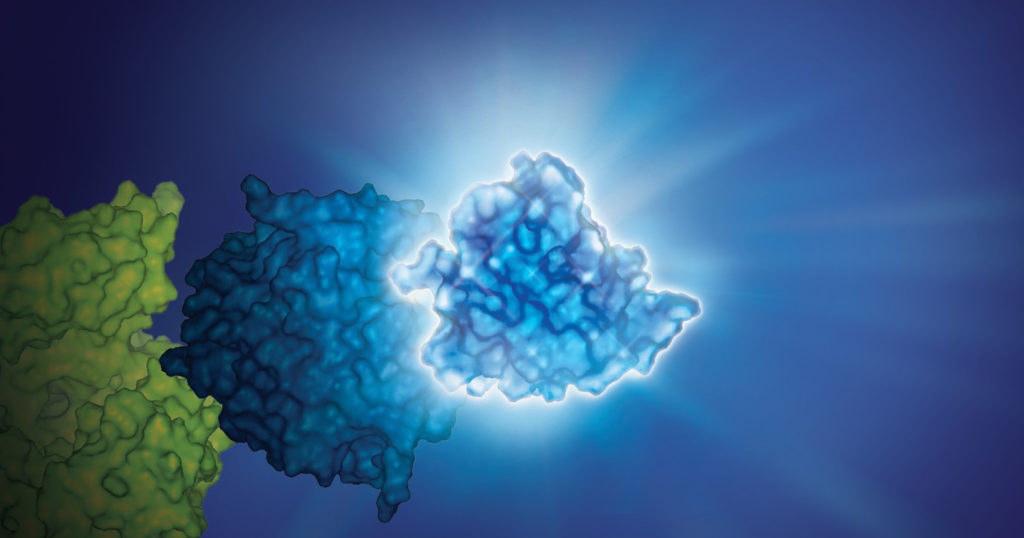
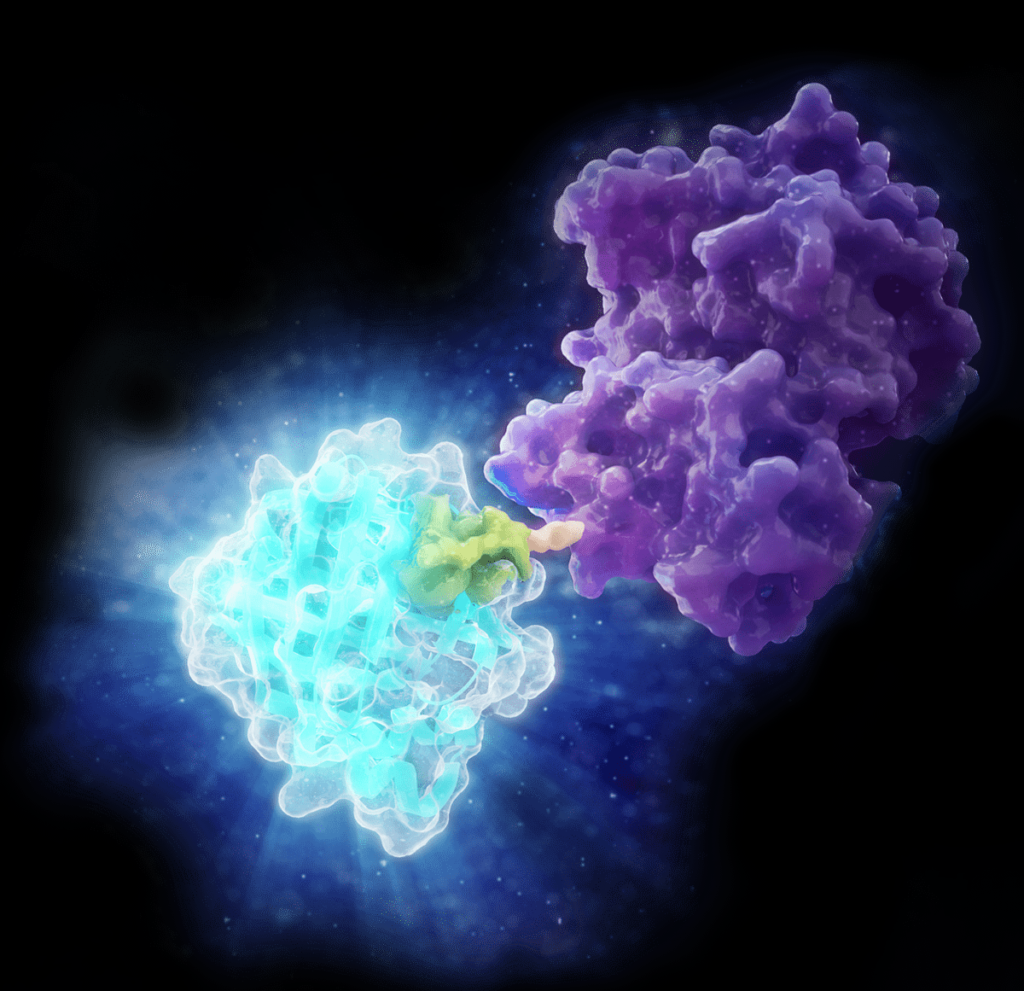
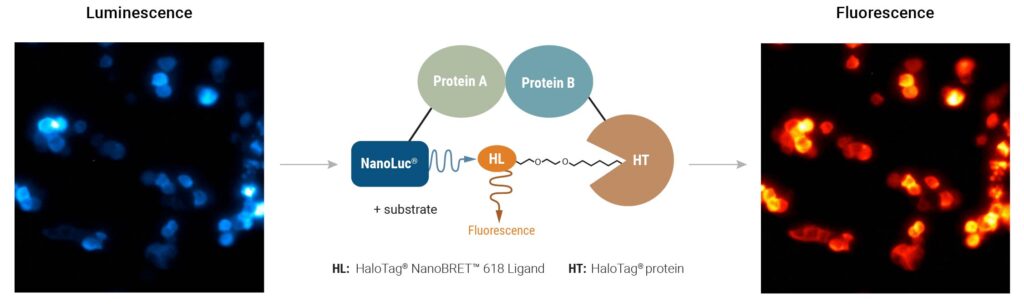
Using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET)-based assays such as NanoBRET® assays allows you to detect protein:protein interactions by measuring energy transfer from a bioluminescent protein donor to a fluorescent protein acceptor. These assays can be used to monitor changes in protein interactions over time, making them a useful tool for small-molecule screening.
The schematic below illustrates how the NanoBRET® NanoGlo® Detection Systems can be used to visualize target engagement. The cells on the left are expressing a NanoLuc® fusion protein, resulting in a luminescent signal. Adding a fluorescent small tracer (center) results in energy transfer and a fluorescent signal (right). Using an imaging platform that has luminescence and fluorescence imaging capabilities will let you see this energy transfer in action.
Bringing the Power of Luminescent Imaging to Your Lab

Having the right tools is critical to unlocking the full potential of bioluminescence imaging. The GloMax® Galaxy Bioluminescence Imager is uniquely positioned to offer researchers the power of imaging in an accessible, benchtop instrument. The Galaxy is a fully equipped microscope that can visualize output from NanoLuc® Technologies and offers luminescence, fluorescence and brightfield imaging capabilities. By offering a user-friendly platform for live-cell luminescent imaging, the GloMax® Galaxy empowers researchers to enrich their understanding of functional and dynamic cellular events across a cell population.
Conclusion
Luminescent imaging can enrich what we learn from live-cell assays and offers an unprecedented view into the dynamics of cellular processes. From monitoring drug responses to visualizing protein interactions, this technology delivers insights that go beyond the capabilities of traditional assays.
Whether you’re studying cancer biology, drug development or cellular signaling, luminescent imaging can help you uncover what’s hidden in your data and see your research in a whole new light.
Additional Resources
GloMax® Galaxy Luminescent Imager, NanoBRET® Nano-Glo® Detection Systems and Nano-Glo® Vivazine live Cell Substrate are for Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.