Originally posted May 25, 2017. Updated 2022
You are studying the effects of a compound(s) on your cells. You want to know how the compound affects cell health over a period of hours, or even days. Real-time assays allow you to monitor cell viability, cytotoxicity and apoptosis continuously, to detect changes over time.
Why use a real-time assay?
A real-time assay enables you to repeatedly measure specific events or conditions over time from the same sample or plate well. Repeated measurement is possible because the cells are not harmed by real-time assay reagents. Real-time assays allow you to collect data without lysing the cells.
Advantages of Real-Time Measurement
Real-time assays allow you to:
- Detect kinetic changes during extended incubations, because cells remain viable when using a real-time cell viability assay. Traditional endpoint assays lyse cells in order to collect data, thus only allow sampling of cells at one time point.
- Perform an extended time study with a single plate, instead of the need to have a separate plate for each time point.
- Use less reagents. A single-plate assay uses fewer cells and plates, also less culture media and other cell culture tools than multiple plates.
- Multiplex your cell viability data with other assays to gain more data from a single plate well. Multiple assays from the same cells provides an internal control and less variability than working with multiple, replicate plates.
Here are some examples of data generated using real-time assays.
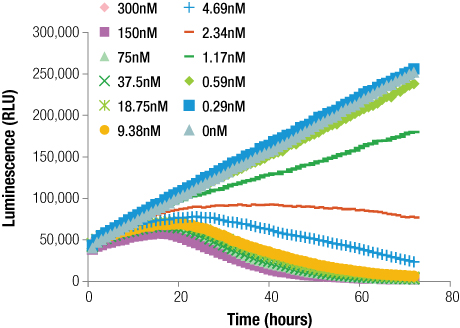
Measuring Cell Viability with Real-Time Assays
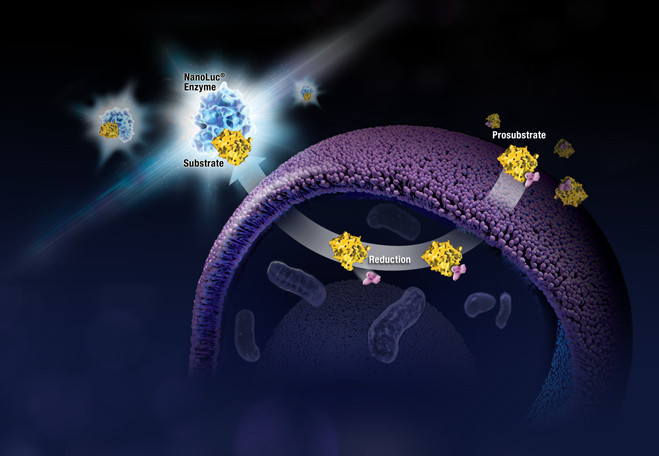
To measure cell viability in real time using a simple, plate-based, bioluminescent method, we used the RealTime-Glo™ MT Cell Viability Assay . RealTime-Glo™ determines the number of viable cells in culture by measuring the reducing potential of cells and thus metabolism. The nonlytic nature of this assay allows the cells to be used for additional downstream applications, including multiplexing with a variety of assay chemistries.
For more details on how the RealTime-Glo™ MT Cell Viability Assay works, watch this animation.
Measuring Cytotoxicity in Real Time
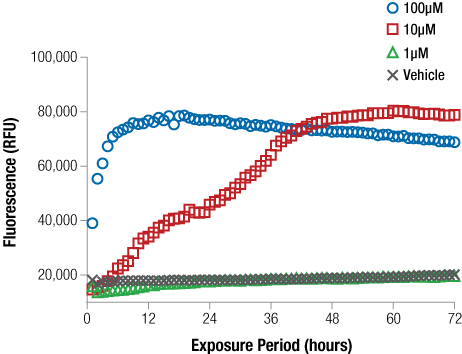
You can detect the accumulation of dead cells in culture via fluorescence, using a plate reader or microscope and the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay. In the following figure, accumulation of dead cells was monitored over 72 hours.
Measuring Immunogenic Cell Death in Real Time
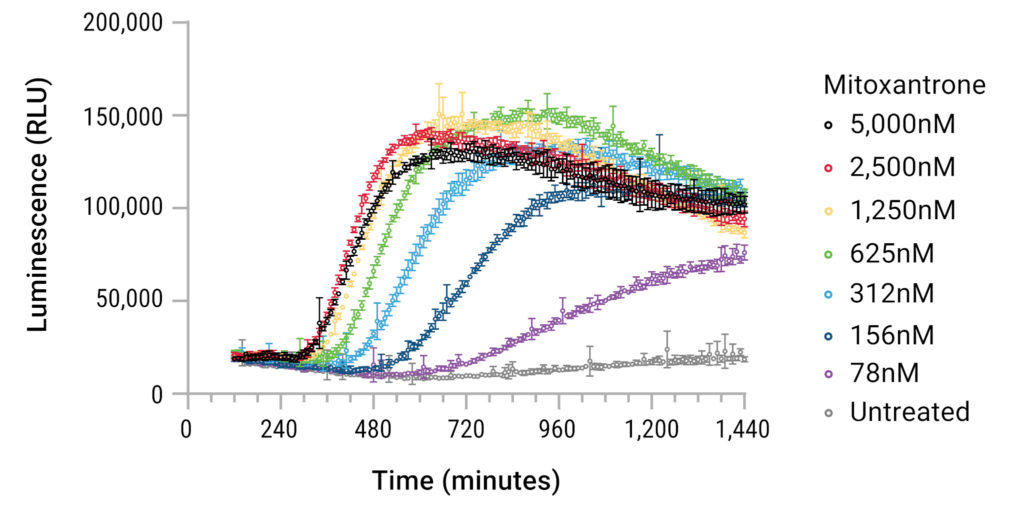
The RealTime-Glo™ Extracellular ATP Assay is a bioluminescent assay designed for kinetic monitoring of ATP released from dying, stressed or activated cells. Extracellular ATP can function as a damage associated molecular pattern (DAMP) and is a key biomarker for determining whether a treatment induces immunogenic cell death, a specialized form of cell death that results in an immune response.
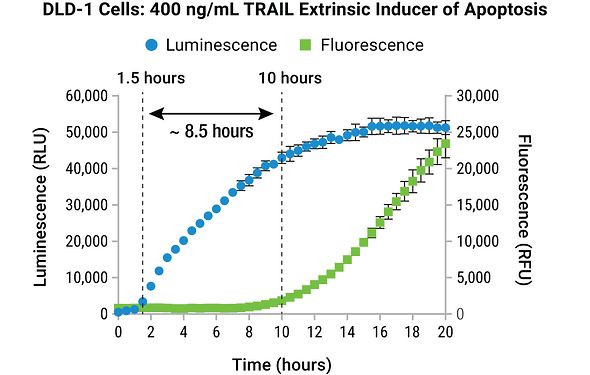
Measuring Apoptosis Using Real-Time Assays
The RealTime-Glo™ Annexin V Apoptosis and Necrosis Assay is a simple, plate-based assay for real-time apoptosis detection. The RealTime-Glo™ Annexin V Apoptosis and Necrosis Assay measures the real-time exposure of phosphatidylserine (PS) on the outer leaflet of cell membranes during the apoptotic process, and it can be scaled for high-throughput applications.
Want more information on the value of real-time assays for your work? We have blogs covering applications of real-time assays right here at Promega Connections.

Do these multiplex assays also work in 3D, e.g. in spheroids of 10000 cells and more?
Yes, the real-time and multiplex assays also work with 3D spheroids. As with many of our cell health assays used with 3D models, you will want to confirm the assay works with your specific model. You can find more information for these assays and others in our 3D Cell Culture Guide. https://www.promega.com/resources/guides/cell-biology/3d-cell-culture-guide/
What about the disadvantages of using real-time assays?