The primary advantage of ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant is that it improves identification of proteins in gel by enhanced protein digestion, increased peptide extraction, and minimized post digestion peptide loss. However, ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant can also facilitate in-solution digestion protocols.
ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant offers two major benefits for digesting proteins in solution.
First, ProteasMAX™Surfactant efficiently solubilizes proteins. In addition, ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant does not interfere with Mass Spec analysis when used in the recommended amount. Mouse membrane proteins can be solubilized with ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant at room temperature in less than 1 hour.
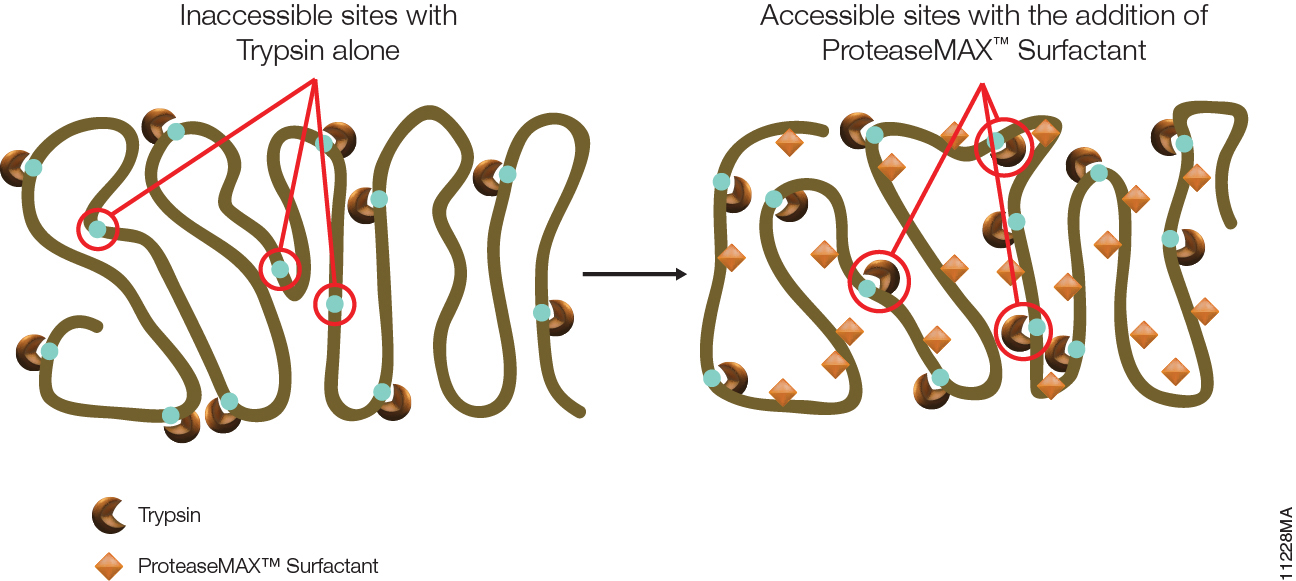
The second advantage of ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant for in-solution protein digestion is an enhanced rate of proteolysis. ProteaseMAX™ Surfactant can partially or fully denature proteins in an SDS-like manner, giving the protease easier access to cleavage sites.
Are you looking for proteases to use in your research?
Explore our portfolio of proteases today.
The following are references:
- Rauniyar, N. et al. (2013) Stable isotope labeling of mammals (SILAM) for in vivo quantitative proteomic analysis. Methods 61, 260–8
- Yim, Y.S. et al. (2013) Sli9trks control excitatory and inhibitory synapse formation witb LAR receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 4057–62.
- Winter, D. and Steen, H. (2011) Optimization of cell lysis and protein digestion protocols for the analysis of HeLa S3 cells by LC-MS/MS. Proteomics 11, 4726–30.
- McNamara, M. et al. (2012) Surface Proteome of Mycobacterium avium during the Early Stages of Macrophage Infection. Infection and Immunity 80, 1868–80.
