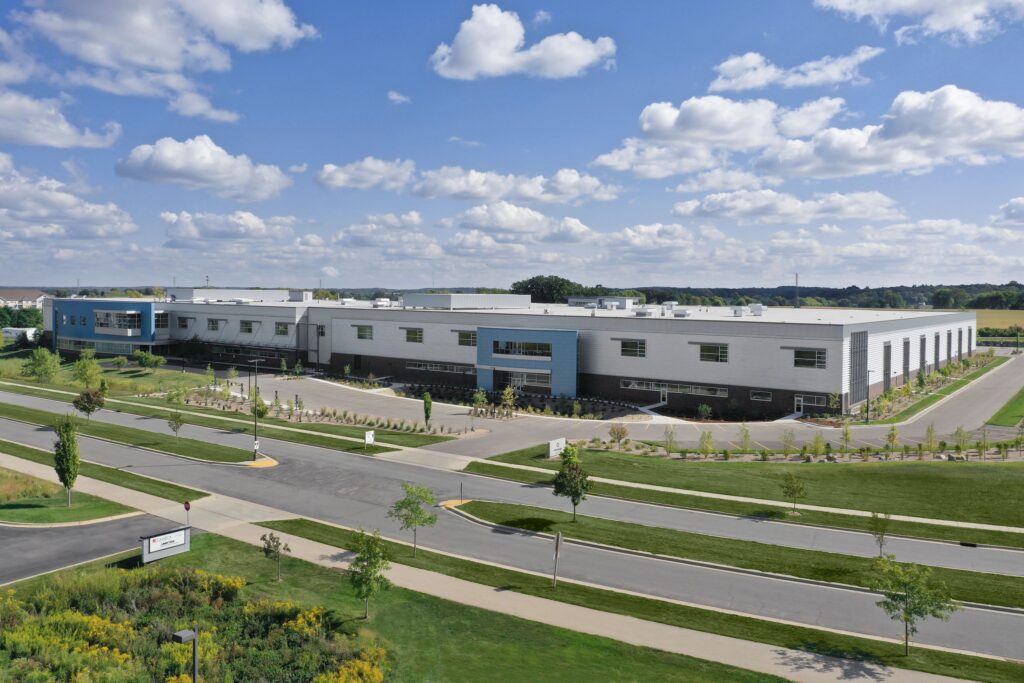
In March 2024, Promega celebrated a significant milestone by completing extensive renovations to Kepler Center, the primary distribution warehouse located at Promega Madison. This massive expansion has increased the facility’s total area to an astounding 320,000 square feet (29,822 square meters).
So, what does this mean for you?
When you place an order from Promega, you can be confident your products will arrive on time. With customers in more than 120 countries, we have built a global logistics network that ensures quality and reliability from the warehouse to your lab. This expansion of Kepler Center enhances our ability to ensure prompt shipping, reaffirming our commitment to timely deliveries.
Delivering Products When You Need Them

Promega Madison ships directly to 40 countries. We maintain close relationships with domestic carriers and international freight forwarders to make sure packages are transported safely and efficiently. Some of these shipments go directly to customer labs, while others will stock distribution facilities around the world.
Promega has additional logistics warehouses strategically located around the world. These warehouses have much of the same capabilities as Kepler Center, such as a range of storage temperature capabilities including ambient, +4°C, -20°C, -70°C and liquid nitrogen cryogenic storage.
Our logistics teams around the world maintain local inventory and oversee the final delivery of orders. We share common processes around the world to ensure quality and continuity throughout the supply chain. These teams also work with our network of distributors to supply products to specific regions.
Our largest logistics facility outside the United States is the EuroHub, located in Walldorf, Germany. This 3,200 square foot (300 square meter) facility acts as a fulfillment agent, managing the entire logistics process to supply customers of every European branch. In 2023, almost 83,000 parcels were dispatched through the EuroHub.
Continue reading “Logistics Built to Deliver: Kepler Center and Beyond”