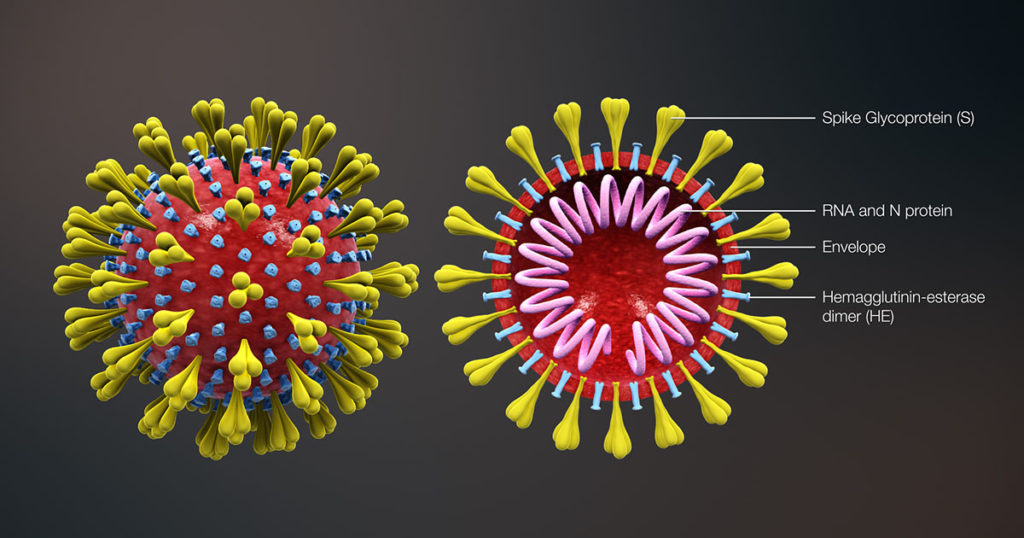
Canine distemper virus (CDV) is a highly contagious pathogen that is the etiological agent responsible for canine distemper (CD), a systemic disease that affects a broad spectrum of both domestic dogs and wild carnivores. While there are commercially available vaccines for CDV that can provide immunity in vivo and protect canines from contracting CD, there is a strong demand for effective canine distemper antivirals to combat outbreaks. Such drugs remain unavailable to date, largely due to the laborious, time-consuming nature of methods traditionally used for high-throughput drug screening of anti-CDV drugs in vitro. In a recent study published in Frontiers in Veterinary Science, researchers demonstrated a new tool for rapid, high-throughput screening of anti-CDV drugs: a NanoLuc® luciferase-tagged CDV.
Continue reading “Barking Up the Right Tree: Using NanoLuc to Screen for Canine Distemper Antivirals”